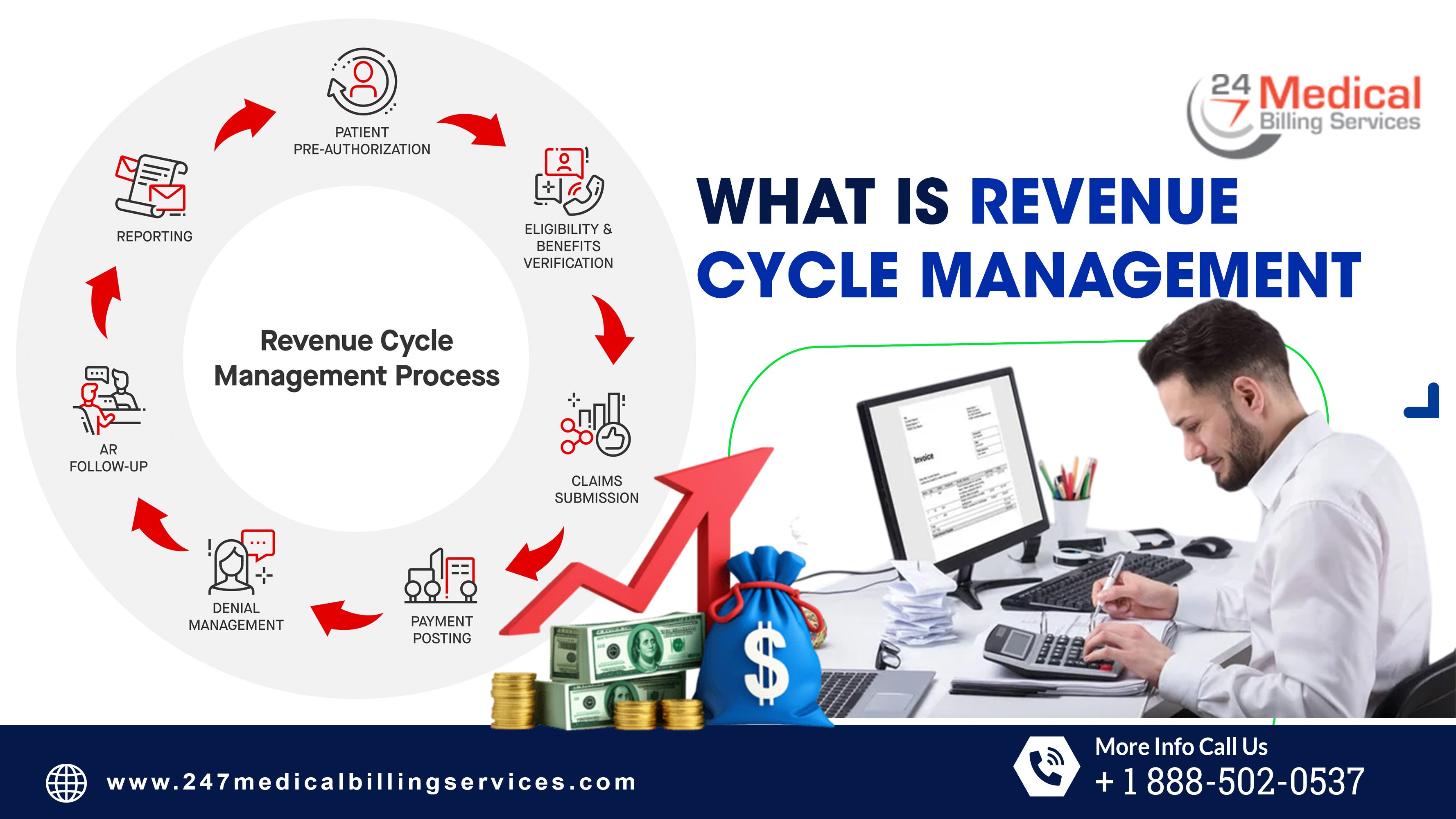
What is Revenue Cycle Management?
Gone are the days when RCM was limited to processing claims and posting payments. It now integrates advanced technologies, data analytics, and value-based care strategies to streamline workflows, minimize revenue leakage, and improve overall financial performance. In fact the market's growth underscores its importance.
The RCM market was valued at USD 172.24 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.1% from 2025 to 2030.
This expansion is driven by the rapid adoption of integrated RCM platforms, which help providers navigate complex billing protocols, reduce denials, and enhance cash flow.
This blog will provide you with a detailed guide on modern revenue cycle management in medical billing.
Key Components of RCM
The revenue cycle is the complete process of managing a patient's financial journey, from initial contact to final payment. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring timely reimbursement and preventing revenue loss.
-
Front-End RCM Processes
This stage involves collecting accurate patient information and preparing for a smooth billing process.
-
Patient Registration and Scheduling
Patient registration captures details such as name, date of birth, address, insurance policy number, and contact information. Whereas scheduling ensures patients are booked efficiently to reduce wait times and avoid missed appointments. Therefore accurate data entry at this stage prevents downstream billing errors and sets the foundation for a clean claim submission.
-
Pre-Authorization and Eligibility Checks
Pre-authorization and eligibility checks confirm whether the patient's insurance plan covers planned services. This process also determines if prior approval is required before treatment. Verifying coverage before the appointment reduces the risk of denials, prevents delays in care and ensures a smooth path toward payment after the service.
-
Upfront Payment Collection
Collecting co-pays, deductibles, and outstanding balances before services are rendered strengthens cash flow and reduces follow-up collection efforts. As a result, the in-house team can clearly explain patient financial responsibilities during check-in. In fact, offering various payment methods, such as online transfers or installment options, makes the process easier for patients and increases the likelihood of timely payments.
-
Mid-Cycle RCM Processes
The mid-cycle stage bridges patient care and the financial process.
-
Clinical Documentation Integrity (CDI)
Clinical documentation integrity (CDI) focuses on ensuring healthcare providers record complete and accurate details of each patient encounter. This includes all diagnoses, procedures, and treatments. In fact strong documentation supports proper coding, demonstrates medical necessity, and meets compliance requirements. Therefore clear and detailed records lead to faster payments and reduce disputes from insurance companies.
-
Charge Capture and Review
Charge capture involves recording all services and procedures provided to the patient during their visit. In fact, missing or delayed charges can directly reduce revenue. As a result, automated charge capture tools help match services with billing records. Also, regular reviews ensure no services are overlooked which leads to complete and accurate reimbursement for the provider.
-
Medical Coding Accuracy
Medical coding involves translating patient care details into standardized ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes for billing purposes. These codes determine how insurers process and reimburse claims. In fact, coding errors can cause denials, payment delays, or audits. Thereby, ongoing coder training and regular audits improve accuracy and help maintain consistent, compliant coding practices.
-
Back-End RCM Processes
The back-end stage ensures claims are processed, payments are posted, and outstanding balances are collected.
-
Claims Preparation and Submission
Claims preparation involves reviewing each claim for accuracy, completeness, and compliance with payer rules before submission. In fact, claims are often "scrubbed" to remove errors that could cause denials. Thereby submitting accurate claims promptly helps maintain cash flow. Many providers use clearinghouses to improve claim quality and ensure timely delivery to insurance companies.
-
Payment Posting and Reconciliation
Payment posting is the process of applying payments from insurers to the correct patient accounts. Whereas reconciliation involves verifying that payments match expected amounts and resolving discrepancies. This step quickly identifies underpayments or missed claims, prevents revenue loss, and keeps financial records accurate for better cash flow and informed decision-making.
-
Denial Prevention and Appeals
Denial prevention involves identifying the reasons for claim rejections and addressing them before resubmission. Further, appeals require correcting errors and providing additional documentation if necessary. As a result, tracking patterns in denials helps address recurring issues. In fact a proactive approach to denial management reduces lost revenue, speeds up payment, and strengthens the overall revenue cycle.
-
Patient Billing and Follow-Up
Patient billing begins after insurance payments are processed, and the remaining balance is assigned to the patient. Sending clear and detailed statements improves understanding and trust. In fact offering convenient payment options and regular reminders encourages timely payments. Therefore good communication reduces disputes and helps maintain positive relationships while recovering outstanding balances efficiently.
RCM KPIs You Should Track
To manage a medical billing process effectively, it is important to monitor specific performance metrics known as key performance indicators (KPIs). These indicators reveal what is working, highlight areas of revenue loss, and guide improvements.
-
Clean Claim Rate (CCR)
The clean claim rate measures the percentage of claims submitted without any errors that payers accept on the first attempt. A high CCR means fewer claim rejections, less time spent on rework, and faster payments.
-
Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R)
Days in accounts receivable measure the average number of days it takes to collect payment after services are provided. Fewer A/R days indicate a faster collection process and healthier cash flow.
-
Denial Rate
The denial rate represents the percentage of claims rejected by insurance companies. A high denial rate often points to problems such as inaccurate coding, insufficient documentation, or unverified patient eligibility.
-
Net Collection Rate
The net collection rate shows the percentage of the total allowable amount that a hospital successfully collects. A high net collection rate indicates strong performance, while a low rate highlights potential issues requiring corrective action.
-
First Pass Resolution Rate (FPRR)
The first pass resolution rate measures the percentage of claims paid without requiring any edits, corrections or resubmissions. A high FPRR means fewer administrative tasks, faster reimbursements, and greater efficiency.
-
Cost to Collect
The cost to collect calculates the total expenses involved in securing payment, including staff wages, technology systems and third-party service fees. A low cost to collect, combined with high accuracy, is ideal.
Conclusion
Effective revenue cycle management is the backbone of a successful medical billing process. Providers can identify revenue leaks, improve operational efficiency, and maintain financial stability by closely monitoring KPIs such as clean claim rate, days in A/R, denial rate, and net collection rate. A well-optimized RCM system ensures timely reimbursements, reduces administrative errors, and strengthens compliance with evolving payer requirements.
However, managing the revenue cycle in-house can be resource-intensive which requires constant staff training and technology investments. Outsourcing RCM to a trusted team like 24/7 Medical Billing Services gives providers access to certified billing professionals, advanced RCM tools, and data-driven insights that enhance collections. With our end-to-end RCM solutions, our team helps healthcare organizations improve claim accuracy and accelerate cash flow.
FAQs
Q1. What is the role of AI in revenue cycle management?
AI automates claim scrubbing, predicts denials, and speeds up payment posting.
Q2. How does real-time eligibility verification improve billing?
It prevents claim denials by confirming coverage before services are provided.
Q3. What is the impact of telehealth on revenue cycle processes?
Telehealth adds new coding requirements and reimbursement rules to manage.
Q4. Why is compliance monitoring important in RCM?
It reduces legal risks and ensures adherence to payer and government rules.
Q5. How can predictive analytics benefit medical billing?
It forecasts payment delays and identifies patterns causing revenue loss.


.png)
